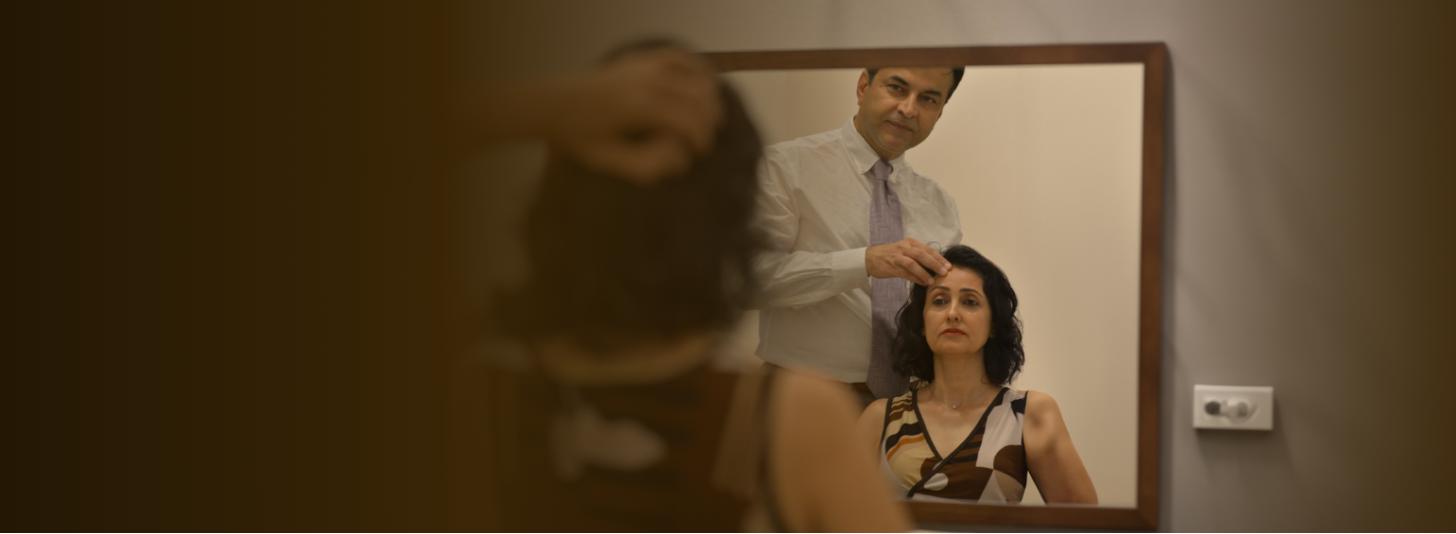





Delivering Excellence in Facial Plastic Surgery
Precision. Passion. Perfection
Safe, Artful Transformations for Your Face
Comprehensive ENT Care for Kids and Adults.
Your Family's ENT Care, Fully Addressed
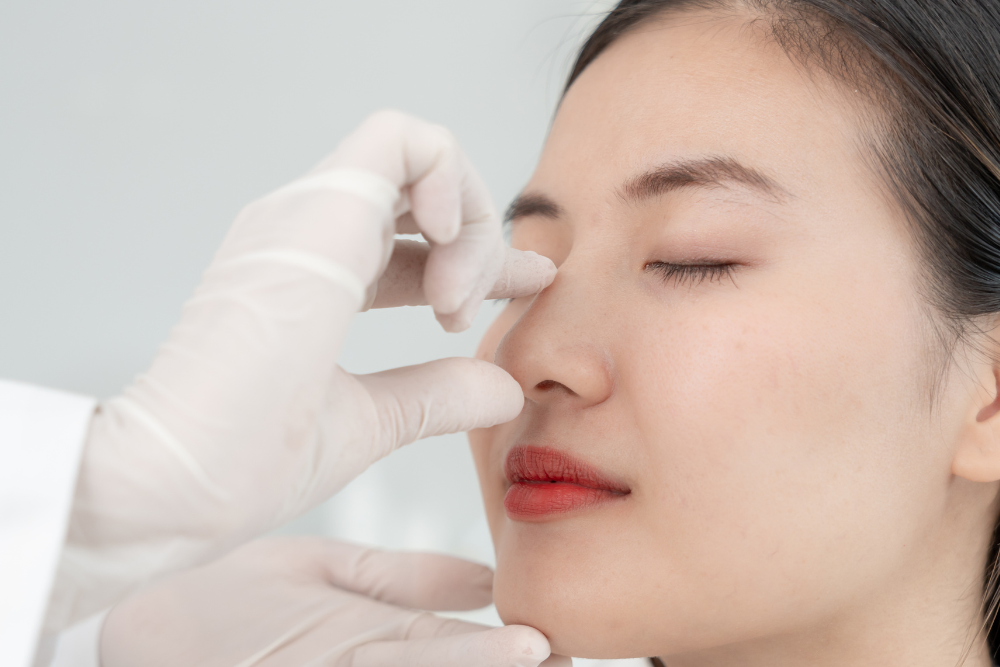
Rhinoplasty: Enhancing Nasal Aesthetics
and Function.
HEARING LOSS TREATMENT IN SINGAPORE
HOW DO WE HEAR?
The sense of hearing is one of the most vital and complex processes that the human body undertakes. Dr Sandeep Uppal and his team at The ENT Clinic are committed to educating patients about the intricacies of the hearing mechanism. Understanding how normal hearing works can provide valuable insights into the diagnosis and treatment of various hearing-related issues.

THE COMPONENTS OF THE EAR
The ear is divided into three primary sections:

Outer Ear
Comprises the pinna and the ear canal. The primary function is to collect sound waves from the environment.
Middle Ear
Contains the eardrum and three small bones known as the ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes).
Inner Ear
Houses the cochlea and the vestibular system, which are responsible for hearing and balance, respectively.
THE JOURNEY OF SOUND
Sound Wave Collection
Sound waves are captured by the pinna (outer ear) and travel down the ear canal.
Eardrum Vibration
The sound waves reach the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. Dr Sandeep Uppal often emphasises the sensitivity of this extremely thin membrane, which is why proper ear care is crucial.
Ossicle Movement
The vibrations are transferred to the three ossicles in the middle ear. These bones amplify the sound waves.
Fluid Movement in Cochlea
The amplified sound waves then travel into the cochlea of the inner ear, creating fluid waves.
Hair Cell Stimulation
Inside the cochlea, hair cells are stimulated by the fluid waves. These cells are the sensory receptors for sound.
Electrical Signal Generation
The movement of the hair cells generates electrical signals.
Transmission to Brain
These electrical signals are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve.
Interpretation
Finally, the brain interprets these signals as sound, allowing us to understand and react to our environment.
IMPORTANCE OF NORMAL HEARING MECHANISM
Understanding the complexities of the hearing mechanism is vital for the identification and treatment of hearing conditions. It also underscores the necessity for regular audiological assessments to ensure optimal ear health.
UNDERSTANDING TYPES OF HEARING LOSS
Hearing loss can be categorized into three main types: each with its unique characteristics and causes.
CONDUCTIVE HEARING LOSS
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there are issues in the outer or middle ear that hinder sound from reaching the inner ear.
Common causes include earwax blockage, ear infections, fluid build-up in the middle ear, or structural abnormalities in the ear canal or middle ear.
People with conductive hearing loss often experience reduced sound volume and may find it difficult to hear faint sounds.
SENSORINEURAL HEARING LOSS
Sensorineural hearing loss results from damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve.
Causes can vary, including aging, exposure to loud noise, certain medications, genetics, or diseases like Meniere’s disease.
Individuals with sensorineural hearing loss often struggle to understand speech, especially in noisy environments, and may perceive sounds as muffled or distorted.
MIXED HEARING LOSS
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
It can result from a variety of factors, including chronic ear infections that lead to damage in both the middle ear and inner ear.
People with mixed hearing loss experience a combination of reduced sound volume and difficulties with clarity and understanding of speech.
COMMON CAUSES OF HEARING LOSS
AGEING
One of the most common factors, age-related hearing loss, often called presbycusis, occurs naturally as one grows older.
NOISE EXPOSURE
Exposure to loud noises, either suddenly or over a prolonged period, can result in temporary or permanent hearing loss.
EAR INFECTIONS
Inflammation and infection in the ear can obstruct sound pathways, leading to conductive hearing loss.
EARWAX BUILD UP
Accumulated earwax can block the ear canal and impede the flow of sound, although this is usually reversible.
GENETIC FACTORS
Some individuals are genetically predisposed to hearing loss and may experience it earlier in life.
MEDICATIONS TOXIC TO INNER EAR
Certain medications can have a detrimental impact on hearing capabilities.
ILLNESSES AND CONDITIONS
- Meniere’s Disease: A disorder of the inner ear affecting hearing and balance.
- Autoimmune Ear Disease: A rare condition where the body’s immune system attacks the inner ear.
- Otosclerosis: An abnormal bone growth in the middle ear that can cause conductive hearing loss.
TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR HEARING AND WELLNESS SINGAPORE
Considering the significant impact and potential health risks associated with hearing loss, seeking specialized care is crucial. If you or someone you know is experiencing hearing difficulties, seek professional evaluation with Dr Sandeep to address the specific type of hearing loss and potential solutions in Singapore.
Don’t delay any further—take proactive steps today to effectively manage hearing loss in Singapore. Our comprehensive approach combines medical expertise with cutting-edge technology, offering a meticulous range of services designed to diagnose and address the root causes of hearing impairment.
Regain control over your hearing and overall health. Act now by scheduling an appointment with Dr Sandeep Uppal at The ENT Clinic through our appointment scheduling or connecting with us via WhatsApp. Your path to improved hearing and a better quality of life begins right here.
Read more on Myringoplasty (Repair of Ear Drum)
Read more on the sudden loss of hearing – causes, diagnosis and more
Explore our other treatments:
Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea, Allergy and Sinus Infections, Nasal Obstruction, Nose Bleeds, Ear Wax, Ear Infection, Tinnitus, Hearing Loss, Dizziness and Balance Problems, Tonsil and Adenoid Issues, Thyroid Nodules, Salivary Gland Tumours, Voice and Swallowing Disorders.


